ナイルレッド
| ナイルレッド | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
9-(Diethylamino)-5H-benzo[a]phenoxazin-5-one | |
別称 Nile red, Nile blue oxazone | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 7385-67-3 |
| PubChem | 65182 |
| ChemSpider | 58681 |
| UNII | P476F1L81G |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL144472 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C20H18N2O2 |
| モル質量 | 318.376 g/mol |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
ナイルレッド(Nile red)またはナイルブルーオキサゾン(Nile blue oxazone)は、親油性の染料である。細胞内脂質の滴を黄色に染色する。最も一般的な溶媒中では蛍光を発しないが、脂質の多い環境では、強い蛍光を発し、深赤色(極性膜脂質)から強い黄金色(細胞内貯蔵中性脂質)まで変化する。ソルバトクロミズムであり、放射光や励起波長は、溶媒の極性に依って変化する[1]。また、極性溶媒中では強い蛍光を発する[2]。
赤色蛍光タンパク質と同じ波長であり、細胞生物学では、蛍光顕微鏡で可視化するための膜染色に用いられる。また、ボトルウォーター内のマイクロプラスチックの感度の高い検出にも用いられる[3][4]。さらに、味、気体、pH等の変化を検知するセンサとして膜を使う可能性も考えられている[5]。
トリグリセリド(中性脂質)に対しては、最大励起波長が約515 nm(緑色)、最大放出波長が約585 nm(黄橙色)である[6]。対照的に、リン脂質(極性脂質)に対しては、最大励起波長が約554 nm(緑色)、最大放出波長が約638 nm(赤色)である[7]。
合成
[編集]ナイルブルーの硫酸溶液を加熱し、酸加水分解することで合成できる[8]。この過程により、イミニウム基をカルボニル基で置き換える。または、2-ナフトール存在下、対応する5-(ジアルキルアミノ)-2-ニトロソフェノールをから、酸触媒でナイルレッド及びその構造アナログ(ナフトオキサジン染料)を合成することができる。共酸化剤を用いないため、収率はほどほどである[9]。ナイルレッドの生成の際に、原料のナイルブルーを完全に排除できないため、純粋なナイルレッドが必要なときには、さらに精製工程が必要である。

-
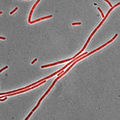
ナイルレッドで膜染色した枯草菌(赤色)
出典
[編集]- ^ Plenderleith, Richard; Swift, Thomas; Rimmer, Stephen (2014). “Highly-branched poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)s with core-shell morphology below the lower critical solution temperature”. RSC Advances 4 (92): 50932-50937. doi:10.1039/C4RA10076J. hdl:10454/11180.
- ^ Greenspan, P; Mayer, E P; Fowler, S D (1 March 1985). “Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets.”. The Journal of Cell Biology 100 (3): 965-973. doi:10.1083/jcb.100.3.965. PMC 2113505. PMID 3972906.
- ^ David Shukman (15 March 2018). “Plastic: WHO launches health review”. BBC News Online
- ^ Mason, Sherri A.; Welch, Victoria G.; Neratko, Joseph (11 September 2018). “Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water”. Frontiers in Chemistry 6: 407. Bibcode: 2018FrCh....6..407M. doi:10.3389/fchem.2018.00407. PMC 6141690. PMID 30255015.
- ^ Khalilian, Alireza; Khan, Md. Rajibur Rahaman; Kang, Shin-Won (1 October 2017). “Highly sensitive and wide-dynamic-range side-polished fiber-optic taste sensor”. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 249: 700-707. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.088.
- ^ “Fluorescence SpectraViewer - Nile Red triglycerides”. Thermo Fisher Scientific (2017年5月17日). 2020年3月6日閲覧。
- ^ “Fluorescence SpectraViewer - Nile Red phospholipids”. Thermo Fisher Scientific (2017年5月17日). 2020年3月6日閲覧。
- ^ Fowler, S. D.; Greenspan, P. (5 January 2017). “Application of Nile red, a fluorescent hydrophobic probe, for the detection of neutral lipid deposits in tissue sections: comparison with oil red O”. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 33 (8): 833-836. doi:10.1177/33.8.4020099. PMID 4020099.
- ^ Park, So-Yeon; Kubota, Yasuhiro; Funabiki, Kazumasa; Shiro, Motoo; Matsui, Masaki (11 March 2009). “Near-infrared solid-state fluorescent naphthooxazine dyes attached with bulky dibutylamino and perfluoroalkenyloxy groups at 6- and 9-positions”. Tetrahedron Letters 50 (10): 1131-1135. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.12.081.