南米諸国連合の加盟国一覧
表示
南米諸国連合 > 南米諸国連合の加盟国一覧
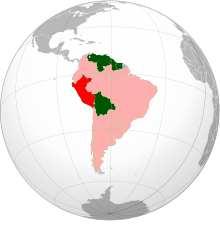
加盟国
一時停止中の加盟国
2018年4月に6つの加盟国が組織への参加を一時停止して以降、南米諸国連合の加盟国は4ヶ国である。エクアドルとウルグアイはそれぞれ2019年3月と2020年3月に離脱を発表した[1][2][3]。
加盟国
[編集]| 旗 | 国 | 首都 | 面積 (km²) |
人口 | 人口密度 (/km²) |
通貨 | GDP per cap. (PPP)[4] |
ジニ係数 | 人間開発指数 | 公用語 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ボリビア Estado Plurinacional de Bolivia Bulivya Mamallaqta Wuliwya Suyu |
スクレ ラパス |
1,098,581 | 9,119,152 | 8.9/km² | ボリビアーノ | 4,575[5] | 57.2[6] | 0.663[7] | スペイン語 ケチュア語 アイマラ語 他の34の言語はボリビアの言語を参照 | |
| ガイアナ Co-operative Republic of Guyana |
ジョージタウン | 214,999 | 858,863 | 3.502/km² | ガイアナ・ドル | 7,004[5] | 43.2[6] | 0.633[7] | 英語 Guyanese Creole 他の11の言語はガイアナの言語を参照 | |
| スリナム Republiek Suriname |
パラマリボ | 163,821 | 470,784 | 2.9/km² | スリナム・ドル | 8,947[5] | 41.5[6] | 0.680[7] | オランダ語 スリナムの言語も参照 | |
| ベネズエラ República Bolivariana de Venezuela |
カラカス | 916,445 | 28,199,822 | 30.2/km² | ボリバル・ソベラノ | 11,726[5] | 49.5[6] | 0.735[7] | スペイン語 他の全ての先住民の言語はベネズエラの言語を参照 |
一時停止
[編集]2018年4月に6つの加盟国が組織への参加を一時停止した[8][9][10][11]。
| 旗 | 国 | 首都 | 面積 (km²) |
人口 | 人口密度 (/km²) |
通貨 | GDP per cap. (PPP)[4] |
ジニ係数 | 人間開発指数 | 公用語 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| アルゼンチン República Argentina |
ブエノスアイレス | 2,780,403 | 43,417,000 | 14.49/km² | アルゼンチン・ペソ | 15,030[5] | 48.8[6] | 0.797[7] | スペイン語 (de facto) 他の公用語はアルゼンチンの言語を参照 | |
| ブラジル República Federativa do Brasil |
ブラジリア | 8,514,877 | 204,451,000 | 22/km² | レアル | 11,065[5] | 55.0[6] | 0.718[7] | ポルトガル語 ブラジル手話 他の公用語はブラジルの言語を参照 | |
| チリ República de Chile |
サンディエゴ | 756,950 | 16,763,470 | 22/km² | チリ・ペソ | 14,939[5] | 52.0[6] | 0.805[7] | スペイン語 (de facto) チリの言語も参照 | |
| コロンビア República de Colombia |
ボゴタ | 1,141,748 | 48,219,827 | 40/km² | コロンビア・ペソ | 9,091[5] | 58.5[6] | 0.710[7] | スペイン語 他の68の言語と方言はコロンビアの言語を参照 | |
| エクアドル República del Ecuador |
キト | 256,370 | 13,922,000 | 53.8/km² | センターボ硬貨 アメリカ合衆国ドル |
8,021[5] | 54.4[6] | 0.720[7] | スペイン語 エクアドルの言語も参照 | |
| パラグアイ República del Paraguay Tetã Paraguái |
アスンシオン | 406,752 | 6,158,000 | 15.6/km² | グアラニー | 4,710[5] | 53.2[6] | 0.665[7] | スペイン語 グアラニー語 パラグアイの言語も参照 | |
| ペルー República del Perú Piruw Ripuwlika Piruw Suyu |
リマ | 1,285,220 | 29,180,900 | 23/km² | ヌエボ・ソル | 9,107[5] | 50.5[6] | 0.725[7] | スペイン語 ケチュア語 アイマラ語 他の全ての先住民の言語はペルーの言語を参照 | |
| ウルグアイ República Oriental del Uruguay |
モンテビデオ | 176,215 | 3,477,779 | 19.8/km² | ウルグアイ・ペソ | 13,961[5] | 47.1[6] | 0.783[7] | スペイン語 ウルグアイの言語も参照 |
2018年8月28日、コロンビアの大統領イバン・ドゥケは、外務大臣カルロス・オルメス・トルヒージョが南米諸国連合に対して、組織から離脱するという意思を正式に通知し、6ヶ月以内に有効になるだろうと発表。ウゴ・チャベスが国際条約の存在を二の次にするために創設した組織と非難し、ベネズエラの独裁と呼ばれたものの共犯と呼んだ[12][13]。エクアドルは2019年3月13日に離脱を発表した[14]。ウルグアイも同様に2020年3月に離脱を発表した[3]。
非加盟国
[編集]オブザーバー
[編集]| 旗 | 国[15] | 首都 | 面積 (km²) |
人口 | 人口密度 (/km²) |
通貨 | GDP per cap. (PPP)[4] |
ジニ係数 | 人間開発指数 | 公用語 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| メキシコ Estados Unidos Mexicanos |
メキシコシティ | 1,972,550 | 112,322,757 | 57/km² | メキシコ・ペソ | 14,151[5] | 51.6[6] | 0.770[7] | スペイン語 (de facto) 他の68の先住民の言語はメキシコの言語を参照 | |
| パナマ República de Panamá |
パナマシティ | 75,517 | 3,405,813 | 44.5/km² | バルボア アメリカ合衆国ドル |
12,242[5] | 54.9[6] | 0.768[7] | スペイン語 |
加盟提案中
[編集]| 旗 | 国[15] | 首都 | 面積 (km²) |
人口 | 人口密度 (/km²) |
通貨 | GDP per cap. (PPP)[4] |
ジニ係数 | 人間開発指数 | 公用語 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| トリニダードトバゴ[16] Republic of Trinidad and Tobago |
ポートオブスペイン | 5,131 | 1,353,895 | 254.4/km² | トリニダード・トバゴ・ドル | 31,933[5] | 39.0[6] | 0.772[7] | 英語 |
注釈
[編集]- ^ https://www.apnews.com/3cc29c66207249e18871ce8daeb56a1e
- ^ https://panampost.com/mamela-fiallo/2019/03/15/ecuador-withdraws-from-unasur-in-stunning-rebuke-to-21st-century-socialism/
- ^ a b “Uruguayan government withdraws from UNASUR and returns to TIAR” (2020年3月11日). 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ a b c d at purchasing power parity, per capita, in internatifhj nal dollars (rounded)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Report for Selected Countries and Subjects IMF
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Human Development Report 2010, United Nations Development Programme. Table 3 has the Gini coefficients by country. The year is not given for the Gini coefficient.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o “Human Development Report 2011”. United Nations (2011年). 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “Paraguay y cinco países de la región anuncian el retiro temporal de la Unasur” (2018年4月20日). 2019年8月17日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “Paraguay y otros cinco países se retiran temporalmente de Unasur” (2018年4月20日). 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “Argentina, Brasil, Chile, Colombia, Paraguay y Perú suspenden participación en bloque Unasur”. Reuters (2018年4月20日). 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “Bolivia takes formal actions to reactivate UNASUR” (2018年4月24日). 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “'En seis meses, Colombia estará oficialmente fuera de Unasur': Duque” (スペイン語). El Tiempo. (2018年8月28日) 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “Iván Duque: Nos retiramos de la Unasur por no denunciar crisis en Venezuela” (スペイン語). El Nacional. (2018年8月28日) 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ “'Ecuador pulls out of South American regional group Unasur”. UPI. (2019年3月14日) 2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ a b “Historia”. Secretary General of UNASUR. 2013年7月9日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2021年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ Johnlall, Raphael (18 July 2013). “Venezuela President Maduro talked energy, transport while in T&T”. Trinidad and Tobago Guardian (Guardian Media) 2021年3月10日閲覧. "Apart from Mercosur, Maduro also invited T&T to be "incorporated" into Union of South American Nations (Unasur) because of its geographical proximity to the South American mainland." Maduro said."
